
UVK help - Registry defrag


UVK's Registry defrag module can help you improve performance by consolidating your registry hives.
This feature can be accessed from the System booster section, by pressing Defragment the registry.
Registry defrag overview
Th Windows registry is a large database that contains most of the information needed for Windows and programs to work properly. For instance, if a program needs to save a setting and remember it later, it will write it in the registry, and read it again later, when needed.
The information contained in the registry database is saved in several files called "hives". These files are located in several places in your hard drive. Information related to a user is saved in a file called ntuser.dat, in the user's profile folder. Information related to all users, or global Windows settings is saved in several files, usually located in C:\Windows\System32\Config.
As Windows and other programs add and remove registry keys and values to the registry, the database gets fragmented, with "holes" of empty data. This increases the size of the registry, and the time needed to access the data in the hives.
Note: This type of fragmentation should not be confused with hard drive fragmentation, even though since defragmenting the registry will create new hive files, it will probably defrag them too.
Defragging the registry consists in saving the data contained in each hive to a new hive, and then replacing the old hive with the new one. Because the data in the new hive is continuous, it will have no fragmentation, or "empty holes".
Replacing the old fragmented hives with the new defragmented ones can only be done in the next boot, because the old hives are currently used by the system. Obviously, any changes made to the registry's old hives after defragging will not be effective after reboot. This is why you need to reboot as soon as possible after the registry defragmentation.
Fragmentation analysis
The fragmentation analysis consists in saving the registry data to new hives, and comparing the size of the old hives with the size of the new ones. This process can take several minutes, depending on the size of the registry, but it is not a waste of time, because it would have to be done, anyway, by the defrag process. If you perform the analysis, the selected hives will be already saved, making the defrag process much faster.
To analyze the fragmentation of your registry, select the keys you wish to analyze, and press the Analyze button.
If HKEY_CURRENT_USER is checked, UVK will analyze the fragmentation of the current user's hive.
If HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE is checked, UVK will analyze the fragmentation of the system registry hives. The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE key consists of several hives: SOFTWARE, SAM, SYSTEM and SECURITY.
You can also analyze the fragmentation of other users hives. Select the desired user in the drop-down box and press the Analyze button in the same group.
After the desired analysis is complete, the fragmentation of the selected hive will be displayed, like in the screenshot below.
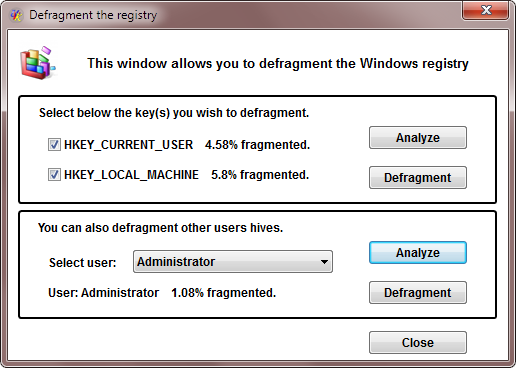
Defragmentation
Select the keys you want to defrag by checking the associated check box. Performing the fragmentaion analysis prior to defragmenting is useful to help you to decide which keys to select, but it is not required.
When ready, press the Defragment button to begin defragging your registry. If you have performed the fragmentation analysis, the defragmentation process will be very fast. Otherwise, it may take several minutes, depending on the registry's size.
You can also defragment other users hives. Select the desired user in the drop-down box and press the Defragment button in the same group.
After the defragmentation is complete, the fields in the dialod box will be updated, reflecting the success of the operation.
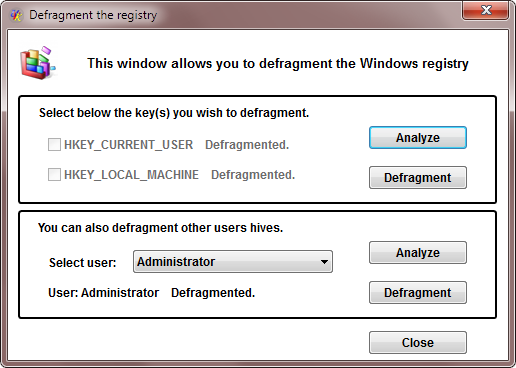
Close Registry defrag
After defragmenting the desired keys, press the Close button. If the defrag process included the HKEY_CURRENT_USER, or the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE key, you will need to reboot the computer in order to complete the operation. In this case you should reboot as soon as possible, because any changes made to the selected registry keys after the defragmentation will not be effective afer the next reboot.
